The Role of Diet in Preventing Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
What's the Deal with Diet and Prostate Cancer?
Let's face it: prostate cancer is a scary thought. But did you know that what you eat plays a surprisingly big role in your risk? It's not a magic bullet, of course, but a healthy diet can be a powerful tool in your arsenal against this disease. We're not talking about extreme diets here; it's more about making smart, sustainable choices that benefit your overall health, and, as a bonus, lower your odds of developing prostate cancer.
The Role of Diet in Preventing Prostate Cancer: Crucial Nutrients
So, what should your plate look like if you're aiming to minimize your prostate cancer risk? Think vibrant colors, a variety of textures, and plenty of nutrients that fight inflammation and support healthy cell growth. Here are some key players:
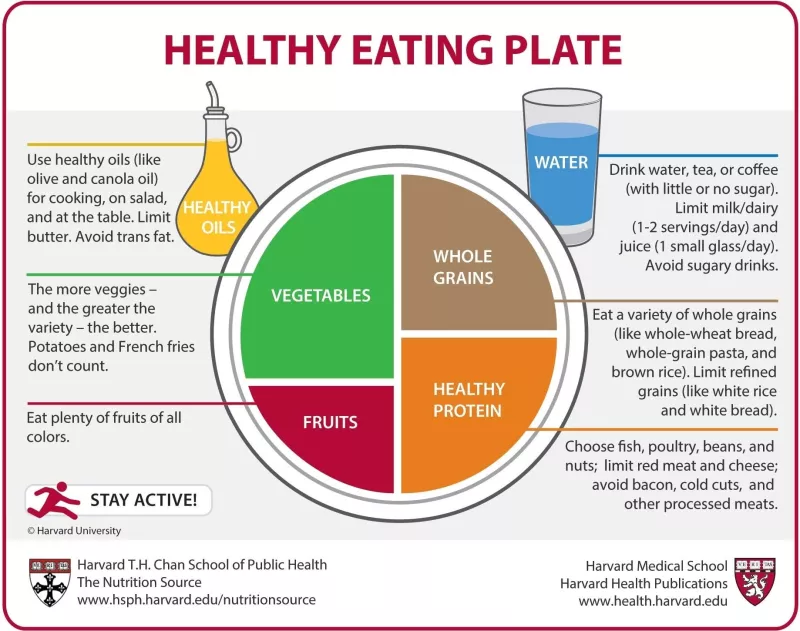
- Fruits and Vegetables: Load up on these! They're packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that protect your cells from damage. Think brightly colored options like berries, tomatoes, broccoli, and leafy greens. The more variety, the better!
- Tomatoes: These are a superstar when it comes to prostate health. They contain lycopene, a powerful antioxidant linked to a reduced risk of prostate cancer.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts—these veggies contain compounds that may help prevent cancer cell growth.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, tuna, and mackerel are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains over refined grains. They provide fiber and other nutrients that support overall health.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are great sources of fiber and plant-based protein.
- Nuts and Seeds: These offer healthy fats, fiber, and vitamins.
The Role of Diet in Preventing Prostate Cancer: Foods to Limit
Just as important as what you *should* eat is what you should *limit*. These dietary choices can increase your risk:
- Red and Processed Meats: Studies have linked high consumption of these to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Try to limit your intake.
- Saturated and Trans Fats: Found in many processed foods and fried foods, these unhealthy fats can fuel inflammation.
- Sugar-Sweetened Beverages: These add empty calories and can contribute to weight gain, a risk factor for prostate cancer.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of various cancers, including prostate cancer. Moderation is key.
The Role of Diet in Preventing Prostate Cancer: Lifestyle Factors
Diet is only one piece of the puzzle. A holistic approach to health includes other lifestyle factors crucial for prostate cancer prevention:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces inflammation.
- Weight Management: Being overweight or obese increases your risk of prostate cancer. Aim for a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact your health. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Regular Checkups: Don't skip your regular checkups with your doctor. Early detection is key to successful treatment.
Beyond the Plate: Supplements and More
While a well-balanced diet is the cornerstone of prostate health, some people consider supplements. However, it's crucial to talk to your doctor *before* taking any supplements, especially those with potential interactions with medications or underlying health conditions. Some commonly discussed supplements include Vitamin D, lycopene, and selenium. Your doctor can help determine if they are appropriate for you and guide you on appropriate dosages. Remember, supplements shouldn't replace a healthy diet – they're a potential *addition*, not a replacement.
Putting it All Together: Creating a Prostate-Protective Diet
Creating a prostate-protective diet doesn't have to be complicated. It's about making gradual, sustainable changes. Think about it like this: it's not about drastic overhauls, but about adding more healthy choices and gradually reducing less-healthy ones. Small changes add up over time. Start by swapping out one unhealthy snack a day for a healthy one. Gradually increase your intake of fruits and vegetables. Small steps lead to big results!
The Role of Diet in Preventing Prostate Cancer: Conclusion
While there's no guarantee against prostate cancer, adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, while limiting red meat, processed foods, and sugary drinks, can significantly reduce your risk. Combine this with a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, stress management, and regular checkups, and you're taking proactive steps towards your well-being. Remember, your journey to better health is a marathon, not a sprint. Be patient with yourself, celebrate small victories, and focus on long-term, sustainable changes.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the best foods to eat to prevent prostate cancer? A diet rich in fruits and vegetables (especially tomatoes and cruciferous vegetables), whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish is ideal. These foods are packed with antioxidants and other nutrients that protect cells from damage.
- Is there a specific "prostate cancer diet"? There isn't one single magic diet, but focusing on a balanced, plant-rich diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting red and processed meats, saturated fats, and sugary drinks is a strong approach.
- Do supplements help prevent prostate cancer? Some supplements like Vitamin D and lycopene are associated with prostate health, but it's crucial to consult a doctor before taking any supplements. Supplements shouldn't replace a healthy diet.
- How much exercise is needed to reduce prostate cancer risk? Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises twice a week.
- Can diet completely prevent prostate cancer? While a healthy diet significantly reduces the risk, it doesn't guarantee complete prevention. Other factors, like genetics, also play a role. However, a healthy diet is an extremely important preventative measure.









No comments